Warm Air vs. Radiant Heaters: Which is Right for Your Factory?
For factory and industrial workshop managers, maintaining optimal temperatures is about more than just comfort; it's a critical factor in staff productivity, machinery performance, and even the quality of finished products. But with various industrial heating systems available, how do you choose the right one?
Two of the most common and effective solutions are warm air heating and radiant heating. While both excel in industrial settings, their operational principles and best-use cases differ significantly. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision for your factory heating solutions.
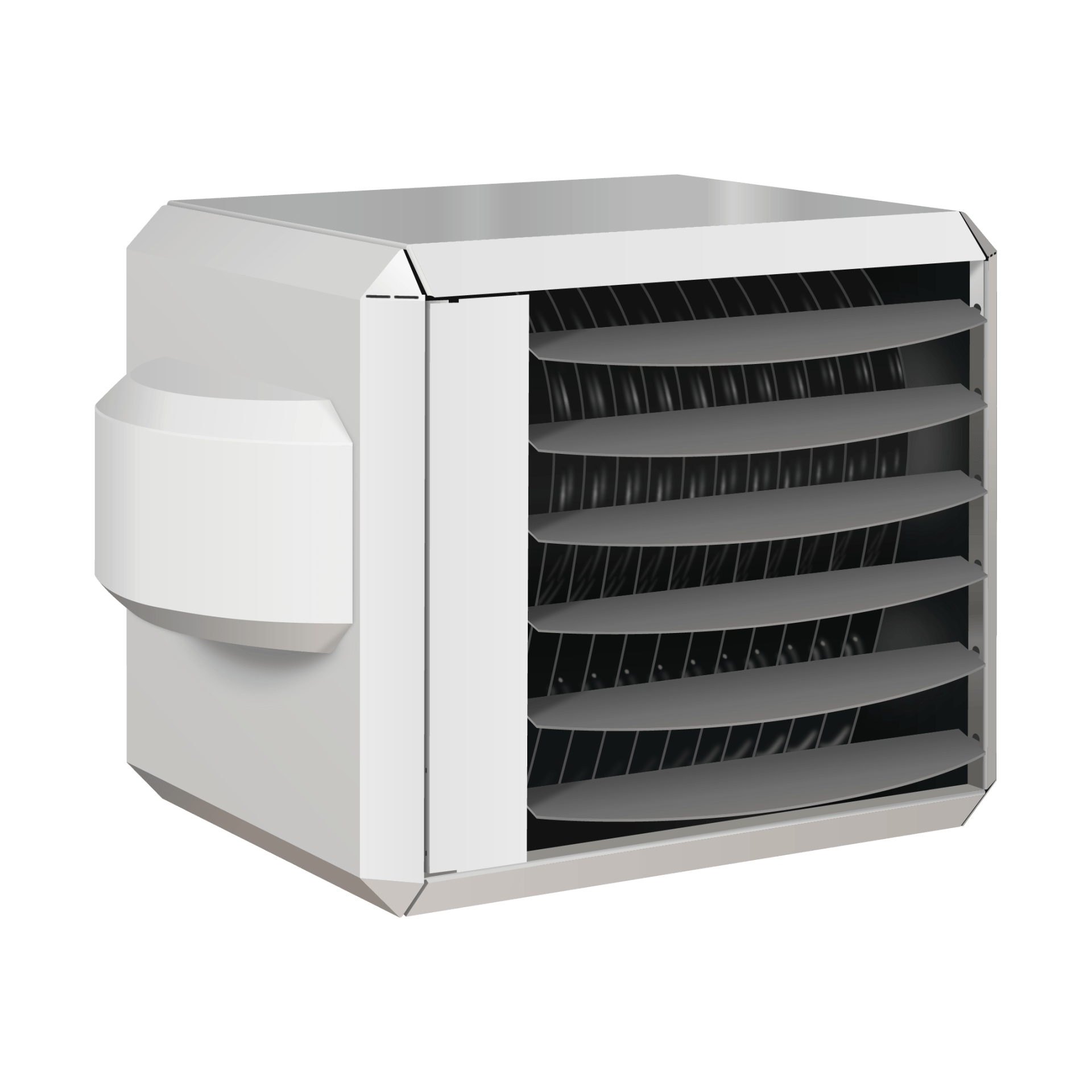
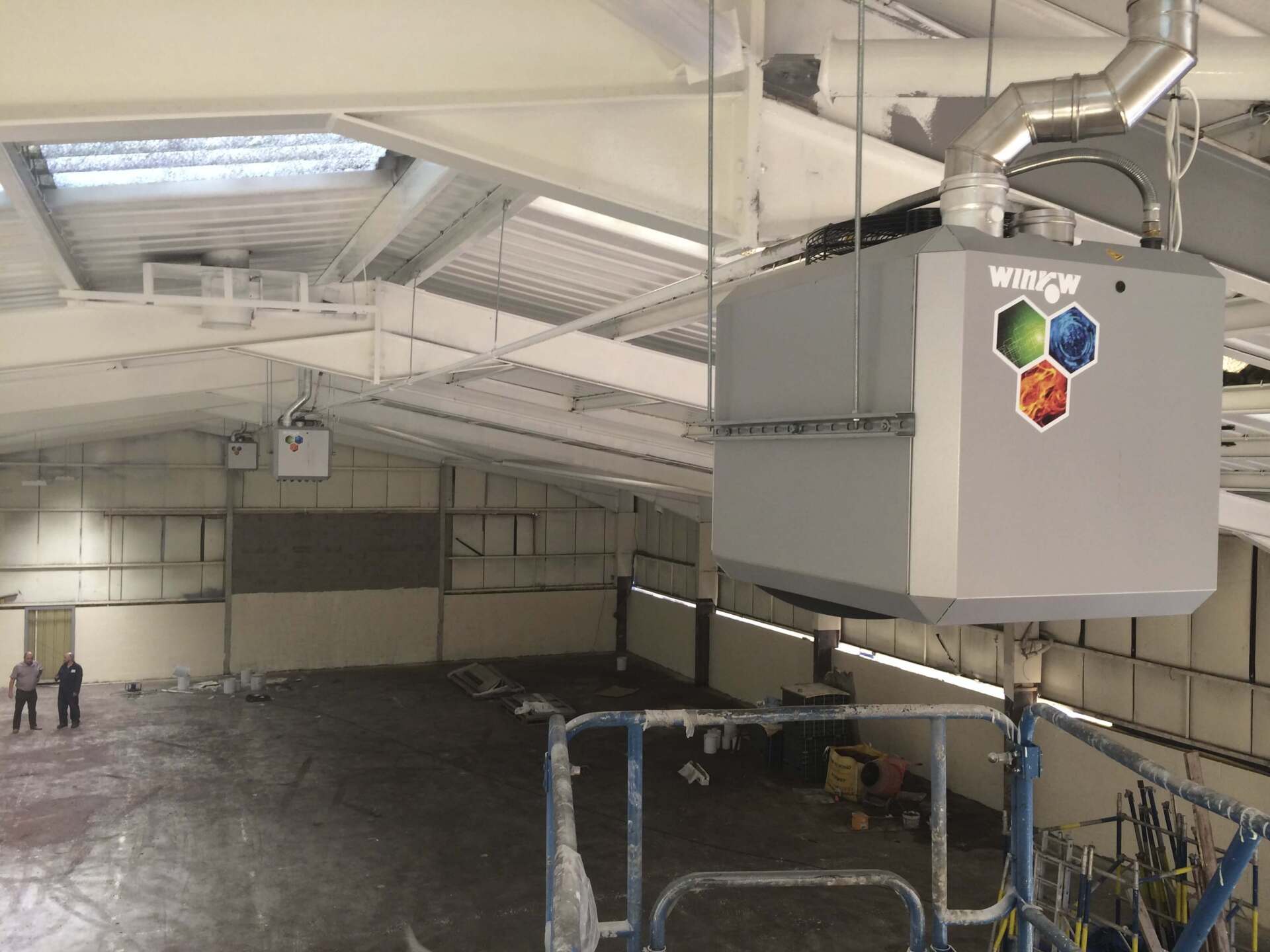
Understanding Warm Air Heating
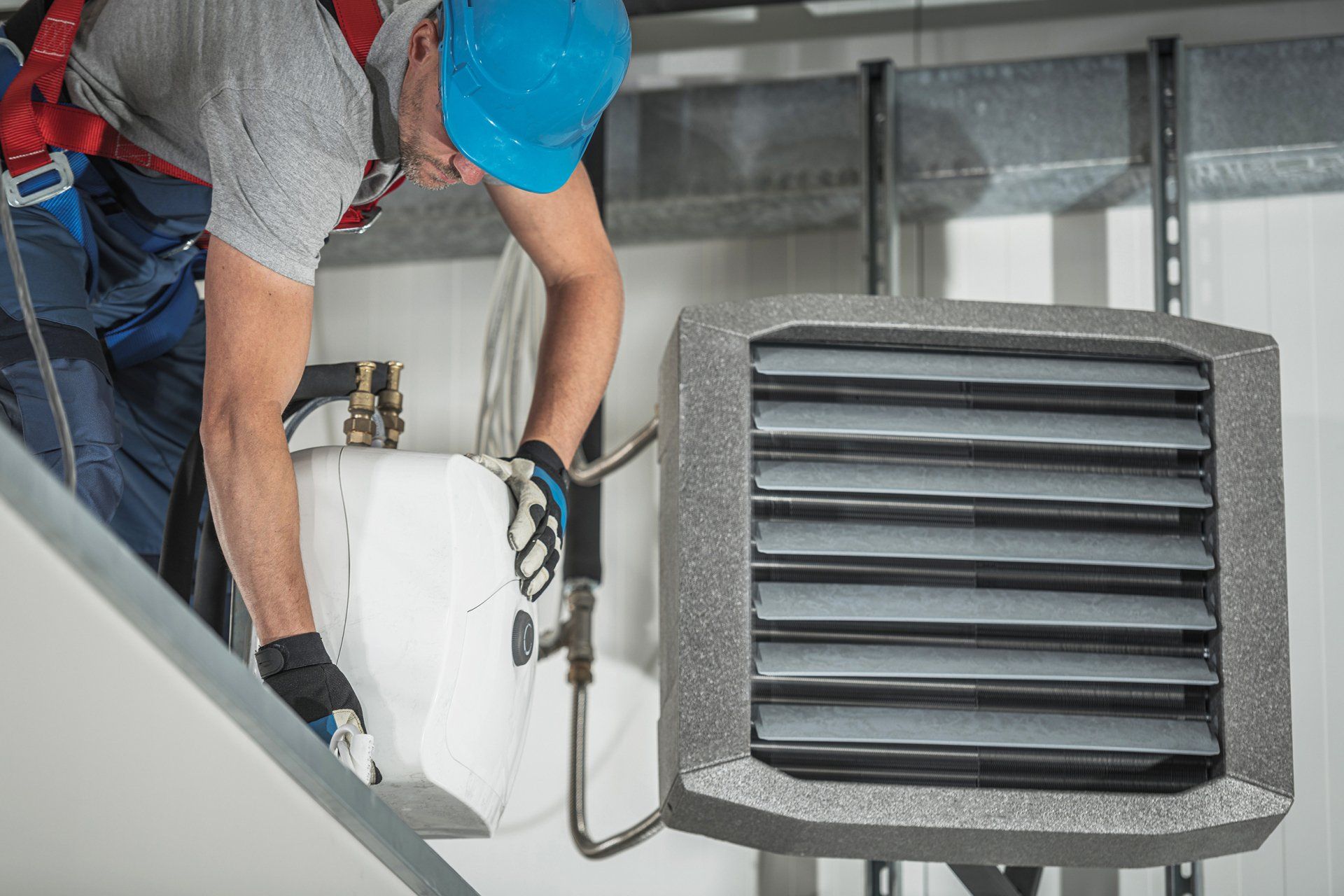
How it Works: Warm air heaters directly heat the air in your facility and then distribute it efficiently through powerful fans. Think of it as a giant, sophisticated fan heater for your entire building.
Best For:
- Large, open-plan factories and workshops: Ideal for uniform heating across vast areas.
- Spaces requiring quick warm-up: Can rapidly bring ambient temperatures up.
- Facilities where a consistent overall temperature is paramount: For general comfort or for certain material storage requirements.
Pros:
- Even Heat Distribution: Excellent for reaching all corners of a large space.
- Rapid Response: Can quickly warm up a cold building.
- Versatile: Modern units are highly efficient and can be fuel-flexible (natural gas, LPG).
Cons:
- Air Movement: Can create air currents which might disturb delicate processes or dusty environments.
- Heat Loss with Open Doors: Warm air escapes quickly when large roller doors are frequently opened.
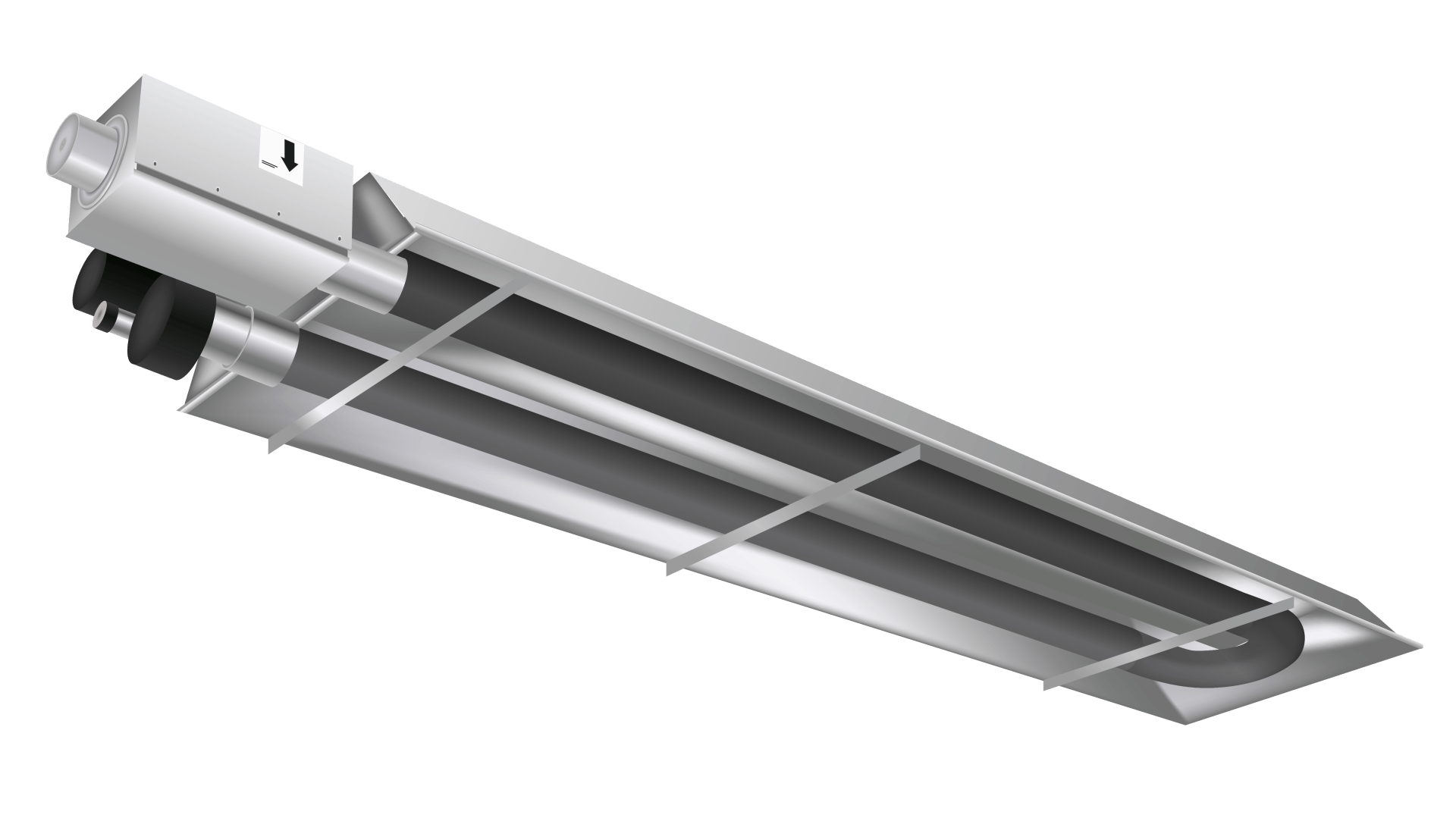
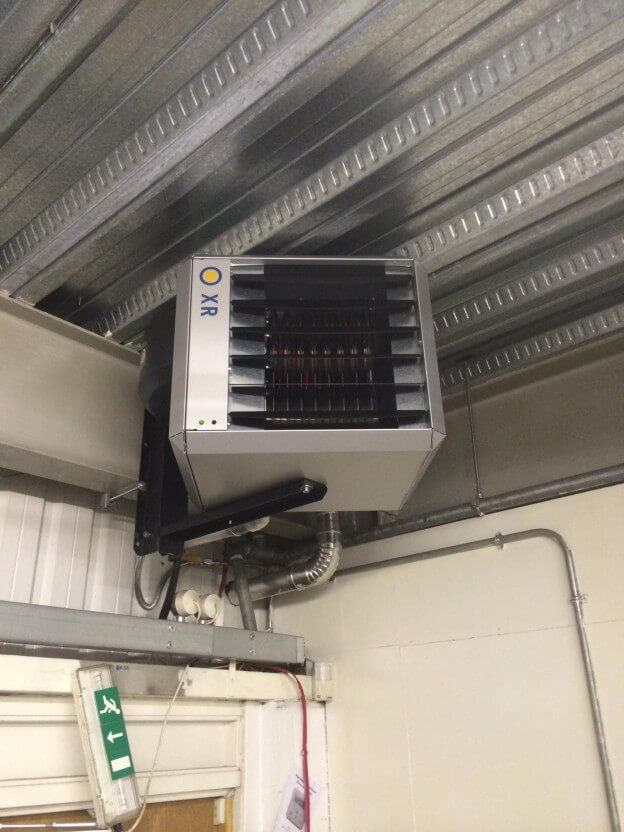
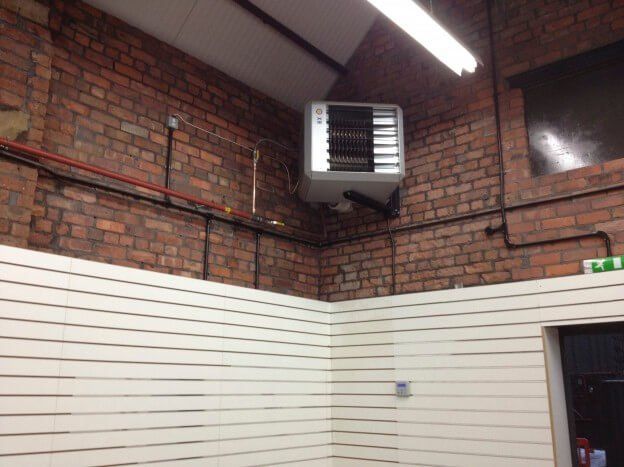
Understanding Radiant Heating
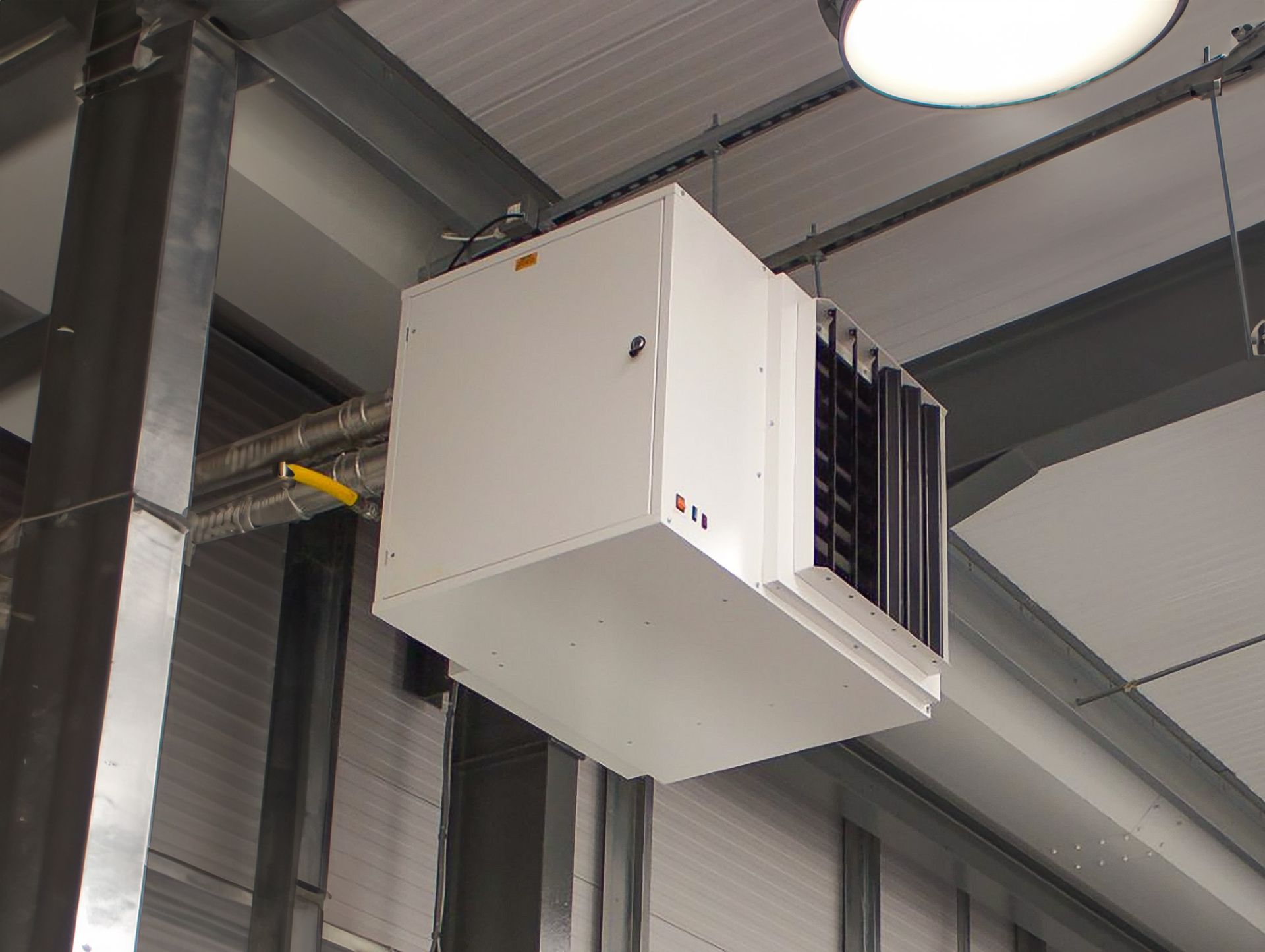
How it Works: Radiant heaters mimic the sun's energy. They emit infrared radiation that directly warms objects, surfaces, and people within their path, rather than heating the air itself.
Best For:
- High-ceilinged factories or workshops: Heat isn't wasted rising to the roof.
- Spot heating specific workstations: Ideal for keeping individual workers comfortable in large, cool areas.
- Buildings with frequent door openings: Direct heat means less energy loss when doors are open.
- Processes requiring direct surface warmth: Can warm materials and machinery.
Pros:
- Energy Efficiency: Highly efficient as it only heats the occupied zone, not the entire air volume.
- Instant Warmth: Provides immediate comfort as soon as it's turned on.
- Minimal Air Movement: Doesn't stir up dust or interfere with air quality.
Cons:
- Line of Sight: Objects in the path are warmed; areas in shadow may not receive direct heat.
- Ambient Air Temperature: May not significantly raise the overall ambient air temperature of a very large space on its own.
Making the Right Choice for Your Factory
The ideal solution often isn't one or the other, but a strategic combination. For example, a large factory might use powerful warm air heaters for ambient temperature control, supplemented by radiant tube heaters over specific workbenches or assembly lines.
A professional design and installation service will conduct a thorough site survey to assess your factory's specific needs, insulation, air movement, and operational patterns. This detailed assessment ensures that the chosen system—whether warm air, radiant, or a hybrid—is perfectly matched to deliver optimal comfort and efficiency for your unique manufacturing environment.
For a deeper dive into all industrial and commercial heating technologies and how to assess your specific requirements, consult our ultimate resource: The Ultimate Guide to Industrial and Commercial Heating Solutions.
Share This Post.
Need a Quote?
Is your business is looking for heating upgrade or an installation quote? Please call us on 08000 588 035 for a free quotation or fill out our contact form and we’ll get back to you as soon as we can.
If you could also attach some relevant images of the building and advise the building volumetric, it will help with our initial design assessment. Thank you.
Winrow - Enquiry Form
Industrial Heating - Latest News
















